产品详情
文献和实验
相关推荐
提供商 :云舟生物科技(广州)股份有限公司
服务名称 :提供定制载体
此价格为VectorBuilder该类型产品标准服务价格,如需个性化定制,请询价概述
我们基于 AAV miR30 的 shRNA 敲低载体系统是一种高效的病毒工具,用于在体外或体内敲低靶基因的表达。由于AAV的免疫原性和细胞毒性低,这是许多动物研究的理想shRNA载体。它利用AAV介导的多顺反子表达盒的递送,该盒由一个或多个基于miR30的shRNA(shRNAmiR)靶向感兴趣的基因和用户选择的ORF组成,其中载体保持为游离体DNA,而不整合到宿主基因组中。shRNAmiR转录本由内源性细胞微RNA途径处理以产生成熟的shRNA,从而促进靶基因mRNA的降解。
首先在大肠杆菌中构建基于AAV miR30的shRNA敲低载体作为质粒。在两个倒置末端重复序列(ITR)之间克隆由一个或多个靶向目标基因的shRNAmiR和用户选择的ORF组成的多顺反子表达盒。然后将其与辅助质粒一起转染到包装细胞中,其中两个倒置末端重复序列(ITR)之间的载体区域被包装成活病毒。放置在两个ITR之间的shRNAmiR表达盒与病毒基因组的其余部分一起被引入靶细胞中。
野生型AAV基因组是一种线性单链DNA(ssDNA),两端有两个ITR形成发夹结构。因此,它也被称为ssAAV。为了在宿主细胞中表达ssAAV载体上的基因,ssDNA基因组需要首先通过两条途径转化为双链DNA(dsDNA):1)以现有的ssDNA基因组为模板,以3' ITR为启动位点,通过宿主细胞的DNA聚合酶机制合成第二链DNA;2)正负链ssAAV基因组之间分子间dsDNA的形成。前者是主导途径。
AAV基因组DNA在宿主细胞核中形成游离体连接体。在非分裂细胞中,这些连接体可以在宿主细胞的一生中保留。在分裂细胞中,AAV DNA通过细胞分裂的稀释效应而丢失,因为游离体DNA不会与宿主细胞DNA一起复制。AAV DNA可以随机整合到宿主基因组中,但极为罕见。这在许多基因治疗环境中是可取的,在这些环境中,载体整合的潜在致癌作用可能引起重大关注。
与利用RNA聚合酶III启动子(如U6)的传统shRNA载体不同,基于miRNA的shRNA系统置于标准RNA聚合酶II启动子的控制之下。这允许使用组织特异性、诱导性或可变强度启动子,从而实现组成型 U6 启动子无法实现的各种实验应用。
相对于其他敲低载体系统,RNA聚合酶II启动子在基于miRNA的shRNA系统中有效转录长转录本的能力也提供了额外的优势。多个shRNAmiR可以转录为单个多顺子,其被加工成细胞内成熟的shRNA。这允许使用单个转录本敲低多个基因或靶向同一基因内的多个区域。因此,该载体可用于表达单个或多个shRNAmiR。其次,在该载体系统中,用户选择的蛋白质编码基因也位于与shRNAmiR相同的多顺子中。该ORF的表达可用于直接监测shRNA转录(如果使用标记ORF),或可用于需要ORF和shRNA共表达的其他目的。
AAV的一个主要实际优势是,在大多数情况下,AAV可以在生物安全1级(BSL1)设施中处理。这是由于AAV本质上缺乏复制,产生很少或没有炎症,并且没有引起已知的人类疾病。
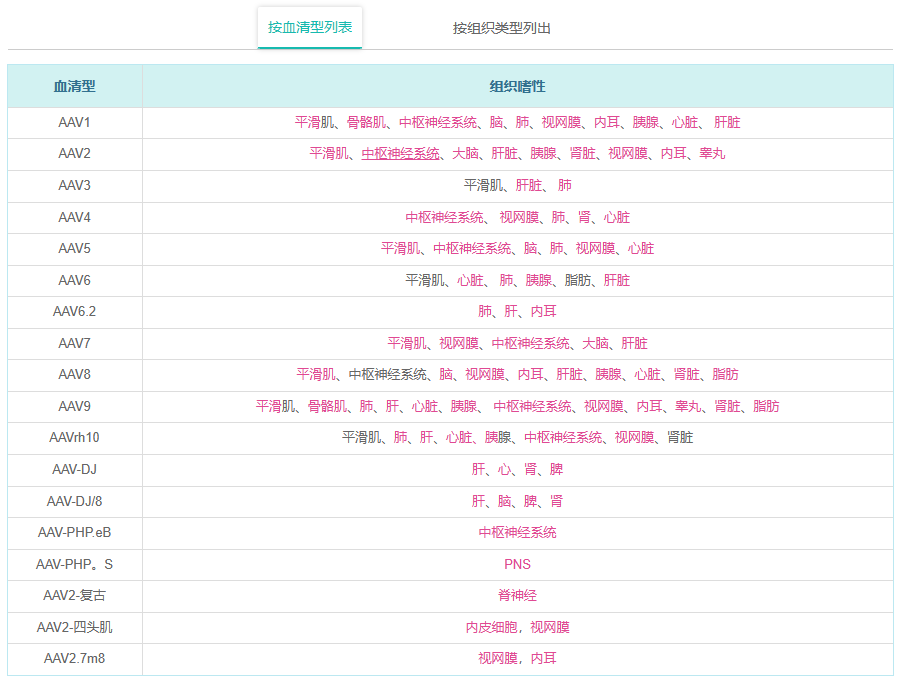
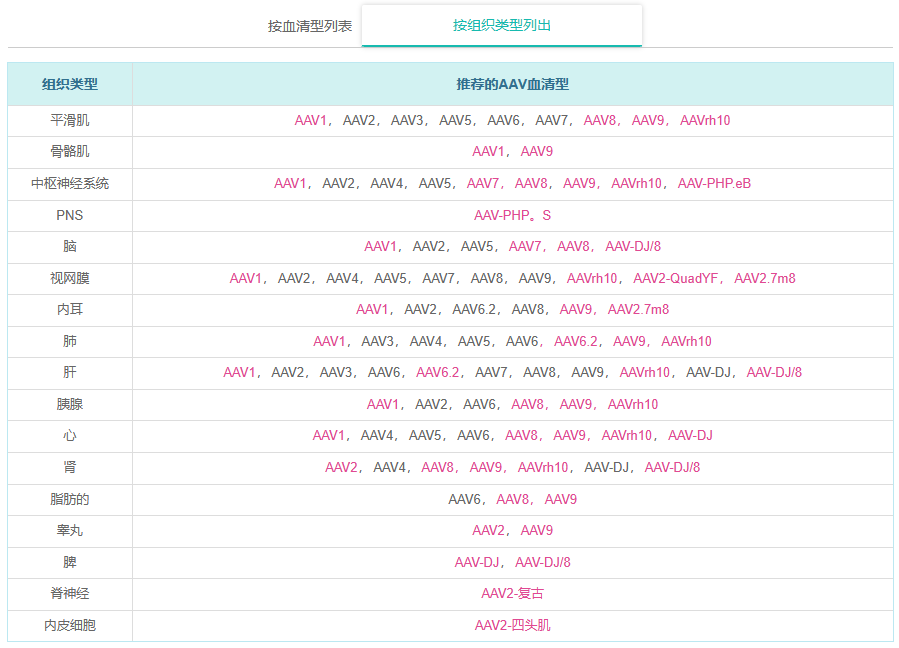
在自然界中已经鉴定出许多AAV菌株。它们根据病毒表面衣壳蛋白的不同抗原性分为不同的血清型。不同的血清型可以使病毒具有不同的组织嗜性(即感染的组织特异性)。当我们的AAV载体被包装成病毒时,通过使用不同的衣壳蛋白进行包装,可以将不同的血清型赋予病毒。下表列出了不同的AAV血清型及其组织嗜性。
多个 shRNA 共表达: 由于RNA聚合酶II有效地转录长RNA,因此多个shRNAmiR可以表达为来自单个启动子的多顺子。因此,该载体可用于表达单个或多个shRNAmiR。
记者ORF的共同表达:用户选择的目的基因或报告基因ORF与shRNAmiR共表达,作为多顺子。这有助于直接监测shRNA转录。
安全: AAV是最安全的病毒载体系统。AAV本质上缺乏复制,并且不知道会导致任何人类疾病。
宿主基因组破坏风险低: 转导到宿主细胞后,AAV载体在细胞核中保留为游离体DNA。缺乏与宿主基因组的整合可能是体内人类应用的理想特征,因为它降低了可能导致癌症的宿主基因组破坏的风险。
高病毒滴度:我们的AAV载体可以包装成高滴度病毒。当通过我们的病毒包装服务获得AAV病毒时,滴度可以达到>1013每毫升基因组拷贝数(GC/毫升)。
广义向性: 当将我们的AAV载体包装成适当的血清型时,可以使用我们的AAV载体轻松转导来自常用哺乳动物物种(如人,小鼠和大鼠)的各种细胞和组织类型。但某些细胞类型可能难以转导,具体取决于所使用的血清型(参见下面的缺点)。
体外和体内有效性: 我们的载体通常用于转导活体动物的细胞,但它也可以在体外有效使用。
技术复杂性: 使用病毒载体需要在包装细胞中产生活病毒,然后测量病毒滴度。与传统质粒转染相比,这些程序在技术上要求很高且耗时。这些需求可以通过在订购载体时选择我们的病毒包装服务来缓解。
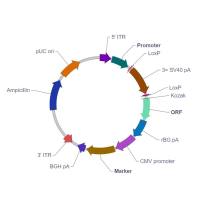
单个 miR30-shRNA AAV shRNA 敲低载体
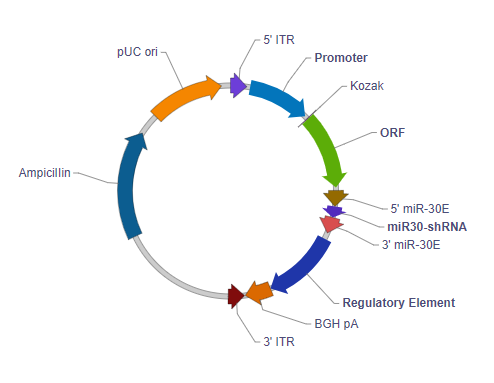
5' ITR: 5' inverted terminal repeat. In wild type virus, 5' ITR and 3' ITR are essentially identical in sequence. They reside on two ends of the viral genome pointing in opposite directions, where they serve as the origin of viral genome replication.
Promoter: Drives transcription of the downstream ORF and shRNAmiR polycistron. This is an RNA polymerase II promoter, rather than an RNA polymerase III promoter such as U6.
Kozak: Kozak consensus sequence. It is placed in front of the start codon of the ORF of interest because it is believed to facilitate translation initiation in eukaryotes.
ORF: The open reading frame of your gene of interest or reporter gene is placed here. This can be used to monitor shRNA expression.
5' miR-30E: An optimized version of the human miR30 5’ context sequence. Facilitates maturation and processing of the shRNA and separation from the tandemly transcribed ORF and other shRNAs.
3' miR-30E: An optimized version of the human miR30 3’ context sequence. Facilitates maturation and processing of the shRNA and separation from the tandemly transcribed ORF and other shRNAs.
miR30-shRNA: This sequence is derived from your target sequence and is transcribed to form the stem portion of the “hairpin” structure of the shRNA.
Regulatory element: Allows the user to add the Woodchuck hepatitis virus posttranscriptional regulatory element (WPRE). WPRE enhances virus stability in packaging cells, leading to higher titer of packaged virus and enhances expression of transgenes.
BGH pA: Bovine growth hormone polyadenylation signal. It facilitates transcriptional termination and polyadenylation of the upstream ORF and shRNAmiR polycistron.
3' ITR: 3' inverted terminal repeat. See description for 5’ ITR.
Ampicillin: Ampicillin resistance gene. It allows the plasmid to be maintained by ampicillin selection in E. coli.
pUC ori: pUC origin of replication. Plasmids carrying this origin exist in high copy numbers in E. coli.
Multiple miR30-shRNA AAV shRNA knockdown vector
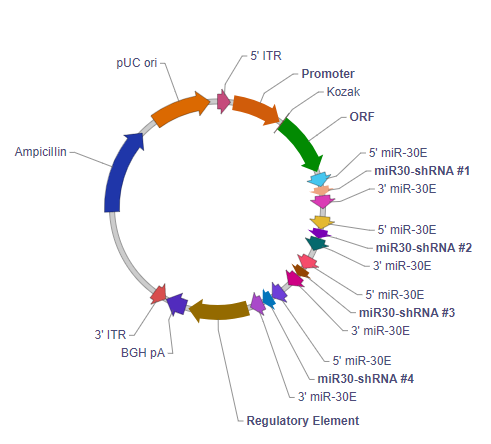
5' ITR: 5' inverted terminal repeat. In wild type virus, 5' ITR and 3' ITR are essentially identical in sequence. They reside on two ends of the viral genome pointing in opposite directions, where they serve as the origin of viral genome replication.
Promoter: Drives transcription of the downstream ORF and shRNAmiR polycistron. This is an RNA polymerase II promoter, rather than an RNA polymerase III promoter such as U6.
Kozak: Kozak consensus sequence. It is placed in front of the start codon of the ORF of interest because it is believed to facilitate translation initiation in eukaryotes.
ORF: The open reading frame of your gene of interest or reporter gene is placed here. This can be used to monitor shRNA expression.
5' miR-30E: An optimized version of the human miR30 5’ context sequence. Facilitates maturation and processing of the shRNA and separation from the tandemly transcribed ORF and other shRNAs.
3' miR-30E: An optimized version of the human miR30 3’ context sequence. Facilitates maturation and processing of the shRNA and separation from the tandemly transcribed ORF and other shRNAs.
miR30-shRNA #1: This sequence is derived from your first target sequence and is transcribed to form the stem portion of the “hairpin” structure of the shRNA.
miR30-shRNA #2: This sequence is derived from your second target sequence and is transcribed to form the stem portion of the “hairpin” structure of the shRNA.
miR30-shRNA #3: This sequence is derived from your third target sequence and is transcribed to form the stem portion of the “hairpin” structure of the shRNA.
miR30-shRNA #4: This sequence is derived from your fourth target sequence and is transcribed to form the stem portion of the “hairpin” structure of the shRNA.
Regulatory element: Allows the user to add the Woodchuck hepatitis virus posttranscriptional regulatory element (WPRE). WPRE enhances virus stability in packaging cells, leading to higher titer of packaged virus and enhances expression of transgenes.
BGH pA: Bovine growth hormone polyadenylation signal. It facilitates transcriptional termination and polyadenylation the upstream ORF and shRNAmiR polycistron.
3' ITR: 3' inverted terminal repeat. See description for 5’ ITR.
Ampicillin: Ampicillin resistance gene. It allows the plasmid to be maintained by ampicillin selection in E. coli.
pUC ori: pUC origin of replication. Plasmids carrying this origin exist in high copy numbers in E. coli.

云舟生物科技(广州)股份有限公司
品牌商实名认证
金牌会员
入驻年限:6年