产品详情
文献和实验
相关推荐
库存 :100
国食药监械注册号 :无
保修期 :12个月
现货状态 :自动型组织切片机,生物组织切片机
供应商 :玉研仪器公司
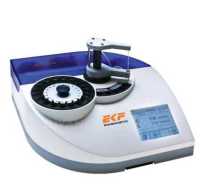
活体组织切片机能够快速连续制备多种活组织切片。
McIlwain 组织切片机是一个快速固定、切片活组织的工具。做工精致,工作稳定,用户数量多,性价比很高。
主要功能:
可用于不冻结的组织或嵌入硬化组织;
可以将组织切割成片状、立体状、动脉环状;
可以用于快速切割多发性脑节,获取肝,肾部分的活细胞,可用于新陈代谢和电生理学研究;
也可用于固定立方体组织或EM;
主要技术参数
| 切片厚度 | 0-1mm可变;最小div.1微米 |
| 切割速度 | 0-200次/分 |
| 最大运行距离 | 25mm |
| 尺寸(W×L×H) | 12.5" ×11" × 6" (32cm×28cm×15cm) |
| 重量 | 14.5 lbs. (6.6 kg) |

工作原理
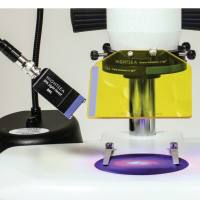
样品需贴上滤纸或塑料光盘(51354)放在操作台上,操作台将在预设的速度下工作。切片厚度可达1毫米。厚度预置了1微米至25微米递增,配有一个安全限位开关,以防止机器超速运行和快速恢复,外层附有白色粉末涂层。
还可以根据需要选择 振动式组织切片机:
振动切片机可用于新鲜的或经过固定的动、植物标本,切片时组织标本不需冰冻或包埋。为此,样品片避免了冰晶破坏,还能保持样品活性和细胞良好形态。给“免疫细胞化学研究”以及“脊髓和脑薄片的神经生物学研究”提供了良好条件。可小动物的脑和脊髓等组织,最薄可切组织厚度接近1微米,新鲜的脑、心、肾等组织最薄可切到30微米,切片完整,片面光滑,染色均匀。
YAN-2028型振动式切片机可以满足神经生理学、神经病理实验病理学 、植物学(根和植物)的高品质切片需求。
要获取新鲜组织的切片,时间和精度都非常重要。2028型振动式切片机操作简单,对进刀速度的调节非常精细,切窗可自由设置,刀片回退速度快速,对新鲜的和经固定的组织样品都能切出厚度均一的切片,即使对一些质地不均且非常难切的组织样品也能达到很好的效果。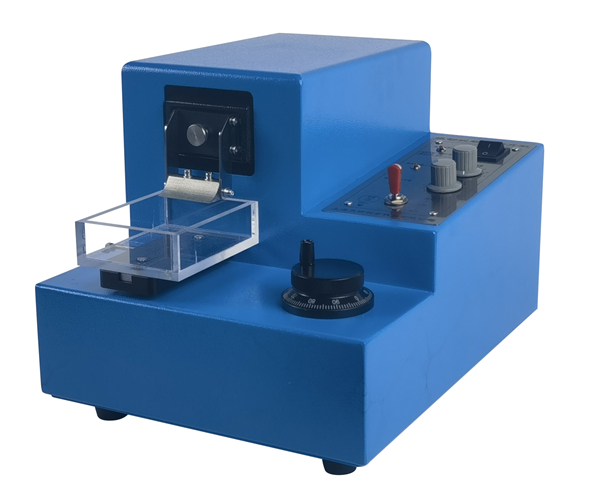
型号:YAN-2028型
主要特点:
· 频率可调:可以在0到100Hz之间调节频率
· 振幅可调:0.2到1mm振幅之间选择适当的振幅
· 进刀速度可调:可以在0.025-2.5mm/s之间精细地调节仪器进刀速度
· 符合人体工效学设计提供更舒适的工作状态
· 方便装载和拆卸刀架
手动切片机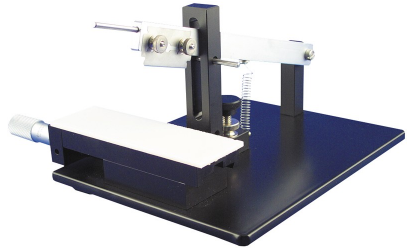
主要特点:
分辨率有两种 10微米 和1微米
部分参考文献:
1.Lee JH, Han J-h, Woo JH, Jou I. 25-Hydroxycholesterol suppress IFN-γ-induced inflammation in microglia by disrupting lipid raft formation and caveolin-mediated signaling endosomes. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 2022;179:252-265.
2.Moreira-de-Sá A, Gonçalves FQ, Lopes JP, et al. Adenosine A2A receptors format long-term depression and memory strategies in a mouse model of Angelman syndrome. Neurobiology of Disease. 2020;146:105137.
3.Martín‐Segura A, Ahmed T, Casadomé‐Perales Á, et al. Age‐associated cholesterol reduction triggers brain insulin resistance by facilitating ligand‐independent receptor activation and pathway desensitization. Aging Cell. 2019;18(3):e12932.
4.Gerace E, Polenzani L, Magnani M, et al. Antidepressant-induced increase in GluA2 expression does not translate in changes of AMPA receptor-mediated synaptic transmission at CA3/CA1 synapses in rats. Neuropharmacology. 2023;223:109307.
5.Di Menna L, Busceti CL, Ginerete RP, et al. The bacterial quorum sensing molecule, 2-heptyl-3-hydroxy-4-quinolone (PQS), inhibits signal transduction mechanisms in brain tissue and is behaviorally active in mice. Pharmacological Research. 2021;170:105691.
6.Ling DSF, Yang L, Goodm*n JH. Brivaracetam prevents the development of epileptiform activity when administered early after cortical neurotrauma in rats. Epilepsia. 2022;63(4):992-1002.
7.Chen T, Noto D, Hoshino Y, Mizuno M, Miyake S. Butyrate suppresses demyelination and enhances remyelination. Journal of Neuroinflammation. 2019;16(1):1-13.
8.Peter E, Hannoun S, Muñiz-Castrillo S, et al. Cerebellar Ataxia With Anti-DNER Antibodies: Outcomes and Immunologic Features. Neurology-Neuroimmunology Neuroinflammation. 2022;9(5).
9.Gasterstädt I, Schröder M, Cronin L, et al. Chemogenetic Silencing of Differentiating Cortical Neurons Impairs Dendritic and Axonal Growth. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience. 2022;16.
10.Roselló-Busquets C, De la Oliva N, Martínez-Mármol R, et al. Cholesterol depletion regulates axonal growth and enhances central and peripheral nerve regeneration. Frontiers in cellular neuroscience. 2019;13:40.
11.Baudouin L, Adès N, Kanté K, et al. Co‐culture of exogenous oligodendrocytes with unmyelinated cerebella: Revisiting ex vivo models and new tools to study myelination. Glia. 2021;69(8):1916-1931.
12.Choi DJ, Yang H, Gaire S, et al. Critical roles of astrocytic‐CCL2‐dependent monocyte infiltration in a DJ‐1 knockout mouse model of delayed brain repair. Glia. 2020;68(10):2086-2101.
13.Dumon C, Pisella L, Diabira D, Belaidouni Y, Wayman GA, Gaiarsa J-L. Developmental switch of leptin action on network driven activity in the neonatal rat hippocampus. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience. 2019;13:254.
14.Vizuete AFK, Fróes F, Seady M, et al. Early effects of LPS-induced neuroinflammation on the rat hippocampal glycolytic pathway. Journal of Neuroinflammation. 2022;19(1):1-23.
15.Cho E, Lee J, Sin JS, et al. Effects of Perilla frutescens var. acuta in amyloid β toxicity and Alzheimer's disease-like pathology in 5XFAD mice. Food and Chemical Toxicology. 2022;161:112847.
16.Subbiah R, Lin EY, Athirasala A, et al. Engineering of an osteoinductive and growth factor‐free injectable bone‐like microgel for bone regeneration. Advanced Healthcare Materials. 2023:2200976.
17.Cho E, Youn K, Kwon H, et al. Eugenitol ameliorates memory impairments in 5XFAD mice by reducing Aβ plaques and neuroinflammation. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 2022;148:112763.
18.Berg EL, Jami SA, Petkova SP, et al. Excessive laughter-like vocalizations, microcephaly, and translational outcomes in the Ube3a deletion rat model of Angelman syndrome. Journal of Neuroscience. 2021;41(42):8801-8814.
19.Gasterstädt I, Jack A, Stahlhut T, Rennau L-M, Gonda S, Wahle P. Genetically encoded calcium indicators can impair dendrite growth of cortical neurons. Frontiers in cellular neuroscience. 2020;14:570596.
20.Ulc A, Zeug A, Bauch J, et al. The guanine nucleotide exchange factor Vav3 modulates oligodendrocyte precursor differentiation and supports remyelination in white matter lesions. Glia. 2019;67(2):376-392.
21.Shyfrin SR, Ferren M, Perrin-Cocon L, et al. Hamster organotypic kidney culture model of early-stage SARS-CoV-2 infection highlights a two-step renal susceptibility. Journal of Tissue Engineering. 2022;13:20417314221122130.
22.Pinto‐Duarte A, Roberts AJ, Ouyang K, Sejnowski TJ. Impairments in remote memory caused by the lack of Type 2 IP3 receptors. Glia. 2019;67(10):1976-1989.
23.Pors SE, Ramløse M, Nikiforov D, et al. Initial steps in reconstruction of the human ovary: survival of pre-antral stage follicles in a decellularized human ovarian scaffold. Human Reproduction. 2019;34(8):1523-1535.
24.Dalmagro AP, Camargo A, Rodrigues ALS, Zeni ALB. Involvement of PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β signaling pathway in the antidepressant-like and neuroprotective effects of Morus nigra and its major phenolic, syringic acid. Chemico-biological interactions. 2019;314:108843.
25.Wellenstein MD, Coffelt SB, Duits DEM, et al. Loss of p53 triggers WNT-dependent systemic inflammation to drive breast cancer metastasis. Nature. 2019;572(7770):538-542.
26.Glykys J, Duquette E, Rahmati N, Duquette K, Staley KJ. Mannitol decreases neocortical epileptiform activity during early brain development via cotransport of chloride and water. Neurobiology of disease. 2019;125:163-175.
27.Celli R, Striano P, Citraro R, et al. mGlu3 metabotropic glutamate receptors as a target for the treatment of absence epilepsy: preclinical and human genetics data. Current neuropharmacology. 2023;21(1):105-118.
28.Horowitz LF, Rodriguez AD, Au-Yeung A, et al. Microdissected “cuboids” for microfluidic drug testing of intact tissues. Lab on a Chip. 2021;21(1):122-142.
29.Wu Q-W, Kapfhammer JP. Modulation of increased mGluR1 signaling by RGS8 protects Purkinje cells from dendritic reduction and could be a common mechanism in diverse forms of spinocerebellar ataxia. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology. 2021;8:569889.
30.Matt L, Pham T, Skrabak D, et al. The Na+-activated K+ channel Slack contributes to synaptic development and plasticity. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. 2021;78:7569-7587.
31.Buonvicino D, Ranieri G, Pratesi S, et al. Neuroprotection induced by dexpramipexole delays disease progression in a mouse model of progressive multiple sclerosis. British journal of pharmacology. 2020;177(14):3342-3356.
32.Camargo A, Dalmagro AP, Altê GA, Zeni ALB, Tasca CI, Rodrigues ALS. NMDA receptor-mediated modulation on glutamine synthetase and glial glutamate transporter GLT-1 is involved in the antidepressant-like and neuroprotective effects of guanosine. Chemico-Biological Interactions. 2023:110440.
33.Wang M, Ramasamy VS, Kang HK, Jo J. Oleuropein promotes hippocampal LTP via intracellular calcium mobilization and Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptor surface recruitment. Neuropharmacology. 2020;176:108196.
34.Templeton AR, Jeffery PL, Thomas PB, et al. Patient-derived explants as a precision medicine patient-proximal testing platform informing cancer management. Frontiers in oncology. 2021;11:5381.
35.Regoni M, Cattaneo S, Mercatelli D, et al. Pharmacological antagonism of kainate receptor rescues dysfunction and loss of dopamine neurons in a mouse model of human parkin-induced toxicity. Cell death & disease. 2020;11(11):963.
36.Lopes JP, Pliássova A, Cunha RA. The physiological effects of caffein* on synaptic transmission and plasticity in the mouse hippocampus selectively depend on adenosine A1 and A2A receptors. Biochemical Pharmacology. 2019;166:313-321.
37.Dietrich M, Koska V, Hecker C, et al. Protective effects of 4-aminopyridine in experimental optic neuritis and multiple sclerosis. Brain. 2020;143(4):1127-1142.
38.Amani M, Lauterborn JC, Le AA, et al. Rapid Aging in the Perforant Path Projections to the Rodent Dentate Gyrus. Journal of Neuroscience. 2021;41(10):2301-2312.
39.Hirukawa A, Singh S, Wang J, et al. Reduction of global H3K27me3 enhances HER2/ErbB2 targeted therapy. Cell Reports. 2019;29(2):249-257.
40.Alhassen W, Kobayashi Y, Su J, et al. Regulation of brain primary cilia length by MCH signaling: evidence from pharmacological, genetic, optogenetic, and chemogenic manipulations. Molecular neurobiology. 2021:1-21.
41.Artinian J, Jordan A, Khlaifia A, et al. Regulation of hippocampal memory by mTORC1 in somatostatin interneurons. Journal of Neuroscience. 2019;39(43):8439-8456.
42.Bevan RJ, Hughes TR, Williams PA, Good MA, Morgan BP, Morgan JE. Retinal ganglion cell degeneration correlates with hippocampal spine loss in experimental Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathologica Communications. 2020;8(1):1-13.
43.Jeon J, Mony TJ, Cho E, et al. Role of extracellular signal-regulated kinase in rubrofusarin-enhanced cognitive functions and neurite outgrowth. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 2022;147:112663.
44.Santos G, Barateiro A, Brites D, Fernandes A. S100B impairs oligodendrogenesis and myelin repair following demyelination through RAGE engagement. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience. 2020;14:279.
45.Delmotte Q, Diabira D, Belaidouni Y, et al. Sonic hedgehog signaling agonist (sag) triggers BDNF secretion and promotes the maturation of GABAergic networks in the postnatal rat hippocampus. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience. 2020;14:98.
46.Rodrigues L, Wartchow KM, Suardi LZ, Federhen BC, Selistre NG, Gonçalves C-A. Streptozotocin causes acute responses on hippocampal S100B and BDNF proteins linked to glucose metabolism alterations. Neurochemistry International. 2019;128:85-93.
47.Joshi DC, Zhang C-L, Mathur D, et al. Tripartite Crosstalk between Cytokine IL-1β, NMDA-R and Misplaced Mitochondrial Anchor in Neuronal Dendrites is a Novel Pathway for Neurodegeneration in Inflammatory Diseases. Journal of Neuroscience. 2022;42(38):7318-7329.
48.Maus L, Lee C, Altas B, et al. Ultrastructural correlates of presynaptic functional heterogeneity in hippocampal synapses. Cell reports. 2020;30(11):3632-3643.
49.Andersen JV, Westi EW, Neal ES, Aldana BI, Borges K. β-Hydroxybutyrate and medium-chain fatty acids are metabolized by different cell types in mouse cerebral cortex slices. Neurochemical Research. 2023;48(1):54-61.
请与我们联系:
TEL: 021-35183767 , 18502129044
QQ: 3007536034
Mail: yuyan0317@126.com
敬请来电咨询!

上海玉研科学仪器有限公司
品牌商实名认证
钻石会员
入驻年限:12年