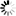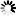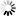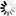产品详情
文献和实验
相关推荐
库存 :10000
保质期 :24个月
供应商 :广州健仑生物科技有限公司
保存条件 : 4-30℃
规格 :25T
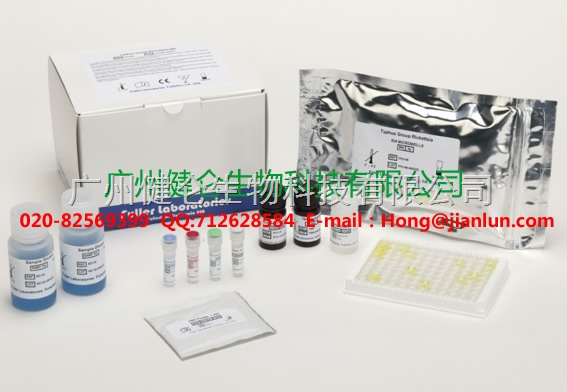
血液检测沙眼衣原体检测卡
广州健仑生物科技有限公司
悉尼隐孢子虫酶联免疫法ELISA检测试剂 我司还提供其它进口或国产试剂盒:登革热、疟疾、流感、A链球菌、合胞病毒、腮病毒、乙脑、寨卡、黄热病、基孔肯雅热、克锥虫病、违禁品滥用、肺炎球菌、军团菌、化妆品检测、食品安全检测等试剂盒以及日本生研细菌分型诊断血清、德国SiFin诊断血清、丹麦SSI诊断血清等产品欢迎致电。
欢迎电话咨询13802525278
欢迎QQ咨询2042552662
血液检测沙眼衣原体检测卡
血液检测沙眼衣原体检测卡
微信二维码扫一扫
【公司名称】 广州健仑生物科技有限公司
【联系电话】 13802525278 020-82574011 杨永汉
【公司传真】 020-32206070
【腾讯 QQ 】 2042552662
【公司地址】 广州清华科技园创新基地番禺石楼镇创启路63号二期2幢101-3室
【企业文化】



宿主经过初次感染产生抗感染抵抗力之后,在一定程度上能坡坏重复感染的虫体,但不能杀伤初次感染的成虫或阻止其产卵。这种现象称为伴随免疫。病理变化血吸虫病的基本病变是由虫卵沉着组织中所引起的虫卵结节。虫卵结节分急性和慢性两种;急性由成熟活虫卵引起,结节中央为虫卵,周围为嗜酸性包绕,聚积大量嗜酸性细胞,并有坏死,称为嗜酸性脓肿,脓肿周围有新生肉芽组织与各种细胞浸润,形成急性虫卵结节。急性虫卵结节形成10天左右,卵内毛蚴死亡,虫卵破裂或钙化,围绕类上皮细胞,异物巨细胞和淋巴细胞,形成假结核结节,以后肉芽组织长入结节内部,并逐渐被类上皮细胞所代替,形成慢性虫卵结节。最后结节发生纤维化。病变部位主要在结肠及肝脏,较多见的异位损害则在肺及脑。1.肠道变病 成虫大多寄生于肠系膜下静脉,移行至肠壁的血管末梢在粘膜及粘膜日本血吸虫日本血吸虫下层产卵,故活组织检查时发现虫卵多排列成堆,以结肠,尤其是直肠、降结肠和乙状结肠为最显著,小肠病变极少,仅见于重度感染者。早期变化为粘膜水肿,片状充血,粘膜有浅溃汤及黄色或棕色颗粒。由于溃汤与充血,临床上见有痢疾症状,此时,大便检查易于发现虫卵。晚期变化主要为肠壁因纤维组织增生而增厚,粘膜高低不平,有萎缩,息肉形成,溃疡、充血、瘢痕形成等复杂外观。血吸虫病变所形成的息肉有转变为癌肿可能,应予重视。由于肠壁增厚,肠腔狭窄,可致机械性梗阻。由于阑尾炎组织也常有血吸虫卵沉着,阑尾粘膜受激及营养障碍,易发生阑尾炎。2.肝脏病变 虫卵随门静脉血流入肝,抵达于门静脉小分枝,在门管区等处形成急性虫卵结节,故在肝表面和切面可见粟粒或绿豆大结节,肝窦充血,肝窦间隙扩大,窦内充满浆液,有嗜酸性粒细胞及单核细胞浸润;肝细胞可有变性,小灶性坏死与褐色素沉着。晚期可见门静脉周围有大量纤维组织增生,形成肝硬变,严重者形成粗大突起的结节。较大门静脉分支管壁增厚,管腔内血栓形成。由于肝内门静脉阻塞,形成门静脉高压,引起腹水、脾肿大及食管静脉曲张。3.脾脏病变 早期肿大,与成虫代谢产物激有关。
After the host has developed an anti-infective resistance through a primary infection, it can, to a certain extent, be able to sway the re-infected worm body, but it cannot kill the first infected adult or prevent its production. This phenomenon is called concomitant immunity. Pathological changes The basic lesion of schistosomiasis is the egg nodule caused by the oocyst tissue. The egg nodule is divided into two kinds: acute and chronic; acute is caused by mature live eggs, the center of the nodule is an egg, surrounded by eosinophilic surrounding, accumulating a large number of eosinophils, and necrosis, called eosinophilic abscess, abscess Around the new granulation tissue and various cell infiltration, the formation of acute egg nodules. The acute egg nodule formed for about 10 days. The ovum within the egg died, the eggs were broken or calcified, surrounded by epithelial cells, foreign giant cells and lymphocytes, and formed pseudotuberculosis nodules. After that, the granulation tissue grew into the interior of the nodule, and gradually Replaced by epithelial cells to form chronic egg nodules. In the final nodule, fibrosis occurred. The lesions are mainly in the colon and liver, and the most common ectopic lesions are in the lungs and brain. 1. Intestinal disease adults mostly parasitize in the inferior mesenteric vein. The blood vessels that migrate to the intestine wall lay eggs in the mucosa and mucous membranes of the Japanese schistosome Schistosoma japonicum. Therefore, during biopsy, it was discovered that the eggs were mostly arranged in heaps to colon, especially the rectum. , descending colon and sigmoid colon is the most significant, minimal intestinal lesions, only seen in severely infected persons. The early changes were mucosal edema, flaking, and pale ulceration of the mucosa and yellow or brown granules. Due to ulceration and congestion, symptoms of diarrhea are clinically observed. At this time, stool examination is easy to detect eggs. The late changes are mainly the thickening of the intestinal wall due to fibrous tissue hyperplasia, mucosal uneven, with atrophy, polyp formation, ulcers, congestion, scar formation and other complex appearance. The polyps formed by schistosome lesions may turn into cancerous lesions and should be taken seriously. Due to thickening of the intestinal wall and narrowing of the intestinal lumen, mechanical obstruction can be caused. Because appendicitis tissue also often has schistosomiasis eggs, appendix mucosal stimulation and nutritional disorders, prone to appendicitis. 2. Liver lesions oocysts flow into the liver with portal venous blood and reach the small branch of the portal vein, forming acute egg nodules in the portal area, etc. Therefore, large nodules of miliary or mung bean are seen on the liver surface and section, hepatic sinus congestion, and hepatic sinusoids The gap is enlarged, the sinus is filled with serous fluid, with infiltration of eosinophils and monocytes; the liver cells may have degeneration, small focal necrosis, and brown pigmentation. In the late stage, a large number of fibrous tissue around the portal vein can be seen to form liver cirrhosis, and in severe cases, large nodules are formed. Larger portal vein branches thicken, and thrombus formation occurs in the lumen. Due to intrahepatic portal vein obstruction, portal hypertension is formed, causing ascites, splenomegaly, and esophageal varices. 3. Splenic lesions are swollen early and are associated with the metabolites of adult metabolites.

广州健仑生物科技有限公司
实名认证
金牌会员
入驻年限:10年