产品详情
文献和实验
相关推荐
国食药监械注册号 :无
库存 :100
供应商 :玉研仪器公司
现货状态 :生物组织切片机,动物组织切片机
保修期 :12个月
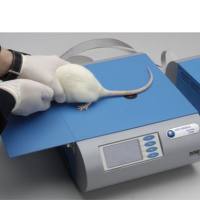
活体组织切片机能够快速连续制备多种活组织切片。
McIlwain 组织切片机是一个快速固定、切片活组织的工具。做工精致,工作稳定,用户数量多,性价比很高。
主要功能:
可用于不冻结的组织或嵌入硬化组织;
可以将组织切割成片状、立体状、动脉环状;
可以用于快速切割多发性脑节,获取肝,肾部分的活细胞,可用于新陈代谢和电生理学研究;
也可用于固定立方体组织或EM;
主要技术参数
| 切片厚度 | 0-1mm可变;最小div.1微米 |
| 切割速度 | 0-200次/分 |
| 最大运行距离 | 25mm |
| 尺寸(W×L×H) | 12.5" ×11" × 6" (32cm×28cm×15cm) |
| 重量 | 14.5 lbs. (6.6 kg) |

工作原理
样品需贴上滤纸或塑料光盘(51354)放在操作台上,操作台将在预设的速度下工作。切片厚度可达1毫米。厚度预置了1微米至25微米递增,配有一个安全限位开关,以防止机器超速运行和快速恢复,外层附有白色粉末涂层。
还可以根据需要选择 振动式组织切片机:
振动切片机可用于新鲜的或经过固定的动、植物标本,切片时组织标本不需冰冻或包埋。为此,样品片避免了冰晶破坏,还能保持样品活性和细胞良好形态。给“免疫细胞化学研究”以及“脊髓和脑薄片的神经生物学研究”提供了良好条件。可小动物的脑和脊髓等组织,最薄可切组织厚度接近1微米,新鲜的脑、心、肾等组织最薄可切到30微米,切片完整,片面光滑,染色均匀。
YAN-2028型振动式切片机可以满足神经生理学、神经病理实验病理学 、植物学(根和植物)的高品质切片需求。
要获取新鲜组织的切片,时间和精度都非常重要。2028型振动式切片机操作简单,对进刀速度的调节非常精细,切窗可自由设置,刀片回退速度快速,对新鲜的和经固定的组织样品都能切出厚度均一的切片,即使对一些质地不均且非常难切的组织样品也能达到很好的效果。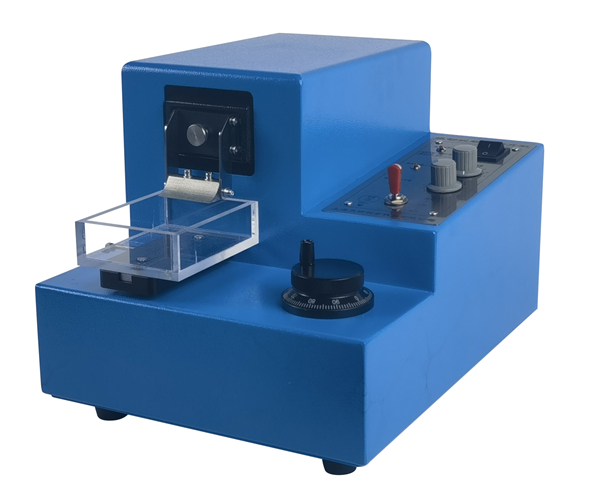
型号:YAN-2028型
主要特点:
· 频率可调:可以在0到100Hz之间调节频率
· 振幅可调:0.2到1mm振幅之间选择适当的振幅
· 进刀速度可调:可以在0.025-2.5mm/s之间精细地调节仪器进刀速度
· 符合人体工效学设计提供更舒适的工作状态
· 方便装载和拆卸刀架
手动切片机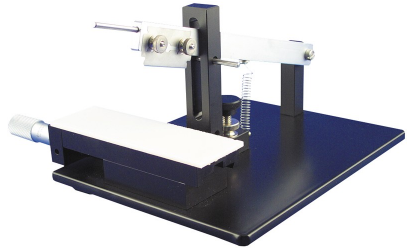
主要特点:
分辨率有两种 10微米 和1微米
部分参考文献:
1.Lee JH, Han J-h, Woo JH, Jou I. 25-Hydroxycholesterol suppress IFN-γ-induced inflammation in microglia by disrupting lipid raft formation and caveolin-mediated signaling endosomes. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 2022;179:252-265.
2.Moreira-de-Sá A, Gonçalves FQ, Lopes JP, et al. Adenosine A2A receptors format long-term depression and memory strategies in a mouse model of Angelman syndrome. Neurobiology of Disease. 2020;146:105137.
3.Martín‐Segura A, Ahmed T, Casadomé‐Perales Á, et al. Age‐associated cholesterol reduction triggers brain insulin resistance by facilitating ligand‐independent receptor activation and pathway desensitization. Aging Cell. 2019;18(3):e12932.
4.Gerace E, Polenzani L, Magnani M, et al. Antidepressant-induced increase in GluA2 expression does not translate in changes of AMPA receptor-mediated synaptic transmission at CA3/CA1 synapses in rats. Neuropharmacology. 2023;223:109307.
5.Di Menna L, Busceti CL, Ginerete RP, et al. The bacterial quorum sensing molecule, 2-heptyl-3-hydroxy-4-quinolone (PQS), inhibits signal transduction mechanisms in brain tissue and is behaviorally active in mice. Pharmacological Research. 2021;170:105691.
6.Ling DSF, Yang L, Goodm*n JH. Brivaracetam prevents the development of epileptiform activity when administered early after cortical neurotrauma in rats. Epilepsia. 2022;63(4):992-1002.
7.Chen T, Noto D, Hoshino Y, Mizuno M, Miyake S. Butyrate suppresses demyelination and enhances remyelination. Journal of Neuroinflammation. 2019;16(1):1-13.
8.Peter E, Hannoun S, Muñiz-Castrillo S, et al. Cerebellar Ataxia With Anti-DNER Antibodies: Outcomes and Immunologic Features. Neurology-Neuroimmunology Neuroinflammation. 2022;9(5).
9.Gasterstädt I, Schröder M, Cronin L, et al. Chemogenetic Silencing of Differentiating Cortical Neurons Impairs Dendritic and Axonal Growth. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience. 2022;16.
10.Roselló-Busquets C, De la Oliva N, Martínez-Mármol R, et al. Cholesterol depletion regulates axonal growth and enhances central and peripheral nerve regeneration. Frontiers in cellular neuroscience. 2019;13:40.
11.Baudouin L, Adès N, Kanté K, et al. Co‐culture of exogenous oligodendrocytes with unmyelinated cerebella: Revisiting ex vivo models and new tools to study myelination. Glia. 2021;69(8):1916-1931.
12.Choi DJ, Yang H, Gaire S, et al. Critical roles of astrocytic‐CCL2‐dependent monocyte infiltration in a DJ‐1 knockout mouse model of delayed brain repair. Glia. 2020;68(10):2086-2101.
13.Dumon C, Pisella L, Diabira D, Belaidouni Y, Wayman GA, Gaiarsa J-L. Developmental switch of leptin action on network driven activity in the neonatal rat hippocampus. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience. 2019;13:254.
14.Vizuete AFK, Fróes F, Seady M, et al. Early effects of LPS-induced neuroinflammation on the rat hippocampal glycolytic pathway. Journal of Neuroinflammation. 2022;19(1):1-23.
15.Cho E, Lee J, Sin JS, et al. Effects of Perilla frutescens var. acuta in amyloid β toxicity and Alzheimer's disease-like pathology in 5XFAD mice. Food and Chemical Toxicology. 2022;161:112847.
16.Subbiah R, Lin EY, Athirasala A, et al. Engineering of an osteoinductive and growth factor‐free injectable bone‐like microgel for bone regeneration. Advanced Healthcare Materials. 2023:2200976.
17.Cho E, Youn K, Kwon H, et al. Eugenitol ameliorates memory impairments in 5XFAD mice by reducing Aβ plaques and neuroinflammation. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 2022;148:112763.
18.Berg EL, Jami SA, Petkova SP, et al. Excessive laughter-like vocalizations, microcephaly, and translational outcomes in the Ube3a deletion rat model of Angelman syndrome. Journal of Neuroscience. 2021;41(42):8801-8814.
19.Gasterstädt I, Jack A, Stahlhut T, Rennau L-M, Gonda S, Wahle P. Genetically encoded calcium indicators can impair dendrite growth of cortical neurons. Frontiers in cellular neuroscience. 2020;14:570596.
20.Ulc A, Zeug A, Bauch J, et al. The guanine nucleotide exchange factor Vav3 modulates oligodendrocyte precursor differentiation and supports remyelination in white matter lesions. Glia. 2019;67(2):376-392.
请与我们联系:
TEL: 021-35183767 , 18502129044
QQ: 3007536034
Mail: yuyan0317@126.com
敬请来电咨询!

上海玉研科学仪器有限公司
品牌商实名认证
钻石会员
入驻年限:12年