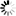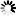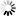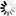Product Pathways - MAPK Signaling
Phospho-c-Fos (Ser32) (D82C12) XP® Rabbit mAb #5348
PhosphoSitePlus® protein, site, and accession data: Fos
| Applications | Reactivity | Sensitivity | MW (kDa) | Isotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| W IP IF-IC F | H M R (Hm) (Mk) (B) (Pg) (Hr) | Endogenous | 62 | Rabbit IgG |
Applications Key: W=Western Blotting IP=Immunoprecipitation IF-IC=Immunofluorescence (Immunocytochemistry) F=Flow Cytometry
Reactivity Key: H=Human M=Mouse R=Rat Hm=Hamster Mk=Monkey B=Bovine Pg=Pig Hr=Horse
Species cross-reactivity is determined by western blot. Species enclosed in parentheses are predicted to react based on 100% sequence homology.
Protocols
Specificity / Sensitivity
Phospho-c-Fos (Ser32) (D82C12) XP® Rabbit mAb detects endogenous levels of c-Fos protein only when phosphorylated on Ser32. The antibody does not cross-react with other Fos proteins, including FosB, FRA1 and FRA2.
Source / Purification
Monoclonal antibody is produced by immunizing animals with a synthetic phosphopeptide corresponding to Ser32 of human c-Fos protein.
Western Blotting

Western blot analysis of extracts from HeLa cells, serum-starved overnight and then either untreated or stimulated for 4 hours with TPA (12-O-Tetradecanoylphorbol-13-Acetate) #4174, using Phospho-c-Fos (Ser32) (D82C12) XP® Rabbit mAb (upper) and c-Fos (9F6) Rabbit mAb #2250 (lower). Antibody phospho-specificity is shown by treating lysates with λ-phosphatase.
Flow Cytometry

Flow cytometric analysis of HeLa cells, untreated (blue) or TPA-treated (green), using Phospho-c-Fos (Ser32) (D82C12) XP® Rabbit mAb.
IF-IC

Confocal immunofluorescent analysis of HeLa cells, serum-starved (left), TPA-treated (middle) or treated with TPA and λ-phosphatase (right), using Phospho-c-Fos (Ser32) (D82C12) XP® Rabbit mAb (green). Actin filaments have been labeled with DY-554 phalloidin (red).
Background
The Fos family of nuclear oncogenes includes c-Fos, FosB, Fos-related antigen 1 (FRA1), and Fos-related antigen 2 (FRA2) (1). While most Fos proteins exist as a single isoform, the FosB protein exists as two isoforms: full-length FosB and a shorter form, FosB2 (Delta FosB), that lacks the carboxy-terminal 101 amino acids (1-3). The expression of Fos proteins is rapidly and transiently induced by a variety of extracellular stimuli including growth factors, cytokines, neurotransmitters, polypeptide hormones, and stress. Fos proteins dimerize with Jun proteins (c-Jun, JunB, and JunD) to form Activator Protein-1 (AP-1), a transcription factor that binds to TRE/AP-1 elements and activates transcription. Fos and Jun proteins contain the leucine-zipper motif that mediates dimerization and an adjacent basic domain that binds to DNA. The various Fos/Jun heterodimers differ in their ability to transactivate AP-1 dependent genes. In addition to increased expression, phosphorylation of Fos proteins by Erk kinases in response to extracellular stimuli may further increase transcriptional activity (4-6). Phosphorylation of c-Fos at Ser32 and Thr232 by Erk5 increases protein stability and nuclear localization (5). Phosphorylation of FRA1 at Ser252 and Ser265 by Erk1/2 increases protein stability and leads to overexpression of FRA1 in cancer cells (6). Following growth factor stimulation, expression of FosB and c-Fos in quiescent fibroblasts is immediate, but very short-lived, with protein levels dissipating after several hours (7). FRA1 and FRA2 expression persists longer, and appreciable levels can be detected in asynchronously growing cells (8). Deregulated expression of c-Fos, FosB, or FRA2 can result in neoplastic cellular transformation; however, Delta FosB lacks the ability to transform cells (2,3).
- Tulchinsky, E. (2000) Histol. Histopathol. 15, 921-928.
- Dobrzanski, P. et al. (1991) Mol. Cell. Biol. 11, 5470-5478.
- Nakabeppu, Y. and Nathans, D. (1991) Cell 64, 751-759.
- Rosenberger, S.F. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274, 1124-1130.
- Sasaki, T. et al. (2006) Mol. Cell 24, 63-75.
- Basbous, J. et al. (2007) Mol. Cell. Biol. 27, 3936-3950.
- Kovary, K. and Bravo, R. (1991) Mol. Cell. Biol. 11, 2451-2459.
- Kovary, K. and Bravo, R. (1992) Mol. Cell. Biol. 12, 5015-5023.
Application References
Have you published research involving the use of our products? If so we'd love to hear about it. Please let us know!
Companion Products
- 2250 c-Fos (9F6) Rabbit mAb
- 2251 FosB (5G4) Rabbit mAb
- 3880 Phospho-FRA1 (Ser265) Antibody
- 5281 FRA1 (D80B4) Rabbit mAb
- 9261 Phospho-c-Jun (Ser63) II Antibody
- 9164 Phospho-c-Jun (Ser73) Antibody
- 9165 c-Jun (60A8) Rabbit mAb
- 7071 Phototope®-HRP Western Blot Detection System, Anti-rabbit IgG, HRP-linked Antibody
- 7074 Anti-rabbit IgG, HRP-linked Antibody
- 7720 Prestained Protein Marker, Broad Range (Premixed Format)
- 7727 Biotinylated Protein Ladder Detection Pack
- 7003 20X LumiGLO® Reagent and 20X Peroxide
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.