产品详情
文献和实验
相关推荐
国食药监械注册号 :无
库存 :100
供应商 :玉研仪器公司
现货状态 :现货
保修期 :12个月
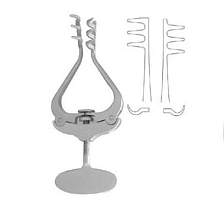
脑立体定位仪 通过加装不同的 适配器,可以扩展定位仪的功能,适应更多的动物种类(多种款式的脑立体定位仪适配器可供选择,敬请来电咨询)小鼠及幼大鼠脑立体定位仪适配器
该小鼠适配器耳杆采用树脂材料,对尖端进行适合的锥度处理,能够牢固的夹紧小鼠头部又避免了采用不锈钢作为耳杆对小鼠颅骨的损伤,两侧耳杆的高度和门齿夹的高度均可自由进行调节,并带有刻度,适合不同的角度进行实验。
小鼠耳棒
保温型 小鼠脑定位仪适配器
增加一台水浴保温主机,可实现对术中的小鼠进行体温维持。
60° 小鼠耳杆
大鼠适配器
· 大鼠适配器是脑立体定位仪的标准配置,通过一对耳杆、鼻和门齿夹固定大鼠头部
· 可以通过燕尾槽上下移动 30mm
· 并具有100um的精度,水平方向可以达到50mm的移动距离,满足不同体重大鼠的固定
· 大鼠适配器默认配置为18度耳杆和门齿夹,可以选配45度耳杆
脑立体定位仪 通过加装不同的适配器,可以扩展定位仪的功能,适应更多的动物种类(多种款式的脑立体定位仪适配器可供选择,敬请来电咨询)

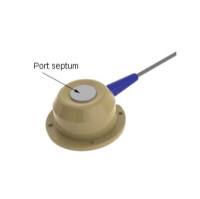
脑立体定位仪麻醉适配器,用于安装在动物脑立体定位仪上,用以进行异氟烷气体麻醉操作的部件。麻醉适配器具体安装在大鼠或小鼠适配器的U型杆上,通过锥形孔将动物的头部固定,气体入口、出口和动物给气口是呼吸联通的,废气出口可连接负压型废气清除器,能够有效减少麻醉气体泄露对研究人员产生影响。
麻醉面罩有大鼠和小鼠两种规格,可配合立体定位仪使用,也可作为一般的动物吸入式麻醉手术使用;
配合脑立体定位仪使用的大小鼠麻醉平台及大小鼠呼吸面罩:
订货信息
| 规格 | 产品名称 |
| 51609M | 定位仪用麻醉面罩-小鼠 |
| 51610 | 定位仪用麻醉面罩-大鼠 |
可根据需要选择小鼠脑立体定位仪、大鼠脑立体定位仪:
小鼠脑立体定位仪 Digital Stereotaxic Instrument 专为新生鼠和其他小型啮齿类动物设计的脑立体定位仪
主要特点:
专为新生鼠和其他小型啮齿类动物设计;
底座上包含两个小鼠定位仪,方便对两只动物进行操作;
两套小鼠耳棒高度可以独立调节,操作臂可全方位定位;
三大技术特色牢固固定小鼠头部:轻质耳棒前端逐渐变细,特殊设计的下颌夹持器,非植入性橡胶头;
两种型号:数显型,带LED显示模块,直接读数,任意点置零,图谱直接定位,分辨率10微米;游标型,分辨率100微米;
其他仪器:大鼠脑立体定位仪,大动物脑立体定位仪,国产脑立体定位仪,进口脑立体定位仪;
大鼠脑立体定位仪
操作灵活、简便,标配大鼠适配器;
脑立体定位仪标尺是由激光雕刻,清晰易读:手动款式精确度为0.1mm,数字显示型号精度为0.01mm;
脑立体定位仪操作臂移动范围(上下,左右,前后):三方向移动距离80mm;
垂直方向可90度转动,并随时锁定位置;
扩充能力很强,可增加操作臂,增加注射装置及颅钻等;
可以根据需要增加不同的固定器,用于多种动物;
脑立体定位仪具有以下优势:
- 标尺易读数
- 移动平滑
- 全方位调节
- 电生理操作方便
- 配件多样,可选配各种动物适配器,麻醉罩以及颅钻
大鼠脑立体定位仪的主要构造: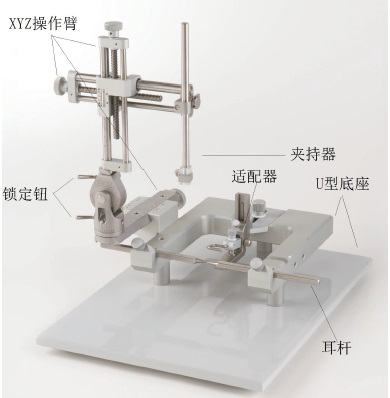
数字显示型脑立体定位仪 Digital Stereotaxic Instrument 是一种可靠的多功能的设备,通过仪器的精准定位,可以确保点击、微管以及其它设备在实验过程中的精确定位。
数显型脑立体定位仪主要特点:
1.适用于小鼠、新生大鼠、鸟类等动物的研究(请根据需求选择合适的配置);
2.无U型底座设计,操作空间最大化;
3.读数精度采用游标卡尺方式,读数精度为10μm;
4.操作臂上下、前后、左右移动范围可达80mm;垂直方向移动90°可锁住;
5.配有鼻子适配器、三种不同型号的耳棒等;
6.三角形的导轨使之能够进行快速定位。其通用的接点便于实验者横向或纵向移动电极,锁定装置能够将电极以任何角度固定,不会滑脱。
7.扩充能力很强,可增加操作臂、增加注射装置及颅钻等,也可以根据需要增加不同的固定器;
8.目标定位的调零功能:在任意一个位点,每条轴方向上的显示都可以归零,这样就可以使操作简化,阅读方便。实际操作中,如果要定位一个特殊位点,可以先找到参考点,然后归零,再移动数显型脑立体定位仪操作臂到希望到达的点上,调低电极,夹持器或微管到位点上即可。

根据需要,还可以选择头部固定器:
大鼠脑部固定器适用于脑部固定的操作实验, 同时配合气体麻醉使用。非常适用于显微镜下对大鼠(小鼠有对应的型号)的手术操作和观察实验使用。我们还可以提供核磁共振兼容型号,供核磁环境中使用。
标准型大鼠头部固定器:
带气体麻醉面罩的大鼠头部固定器: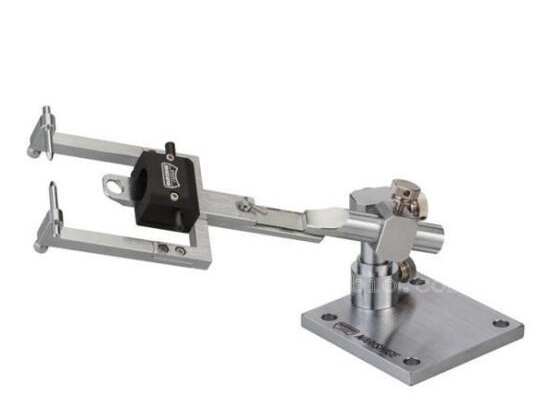
核磁共振环境兼容的大鼠头部固定器: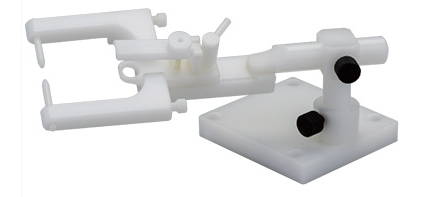

小动物脑立体定位仪部分参考文献:
1. Albéri, L., Lintas, A., Kretz, R., Schwaller, B., & Villa, A. E. (2013). The calcium-binding protein parvalbumin modulates the firing 1 properties of the reticular thalamic nucleus bursting neurons. Journal of neurophysiology, 109(11), 2827-2841.
2. Sonati, T., Reimann, R. R., Falsig, J., Baral, P. K., O’Connor, T., Hornemann, S., Aguzzi, A. (2013). The toxicity of antiprion antibodies is mediated by the flexible tail of the prion protein. Nature, 501(7465), 102-106.
3. Ali, I., O’Brien, P., Kumar, G., Zheng, T., Jones, N. C., Pinault, D., O’Brien, T. J. (2013). Enduring Effects of Early Life Stress on Firing Patterns of Hippocampal and Thalamocortical Neurons in Rats: Implications for Limbic Epilepsy. PLOS ONE, 8(6), e66962.
4. Bell, L. A., Bell, K. A., & McQuiston, A. R. (2013). Synaptic Muscarinic Response Types in Hippocampal CA1 Interneurons Depend on Different Levels of Presynaptic Activity and Different Muscarinic Receptor Subtypes. Neuropharmacology.
5. Bolzoni, F., Bączyk, M., & Jankowska, E. (2013). Subcortical effects of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) in the rat. The Journal of Physiology.
6. Bolzoni, F., Bączyk, M., & Jankowska, E. (2013). Subcortical effects of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) in the rat. The Journal of Physiology.
7. Babaei, P., Tehrani, B. S., & Alizadeh, A. (2013). Effect of BDNF and adipose derived stem cells transplantation on cognitive deficit in Alzheimer model of rats. Journal of Behavioral and Brain Science, 3, 156-161.
8. Gilmartin, M. R., Miyawaki, H., Helmstetter, F. J., & Diba, K. (2013). Prefrontal Activity Links Nonoverlapping Events in Memory. The Journal of Neuroscience, 33(26), 10910-10914.
9. Feng, L., Sametsky, E. A., Gusev, A. G., & Uteshev, V. V. (2012). Responsiveness to nicotine of neurons of the caudal nucleus of the solitary tract correlates with the neuronal projection target. Journal of Neurophysiology, 108(7), 1884-1894.
10. Clarner, T., Diederichs, F., Berger, K., Denecke, B., Gan, L., Van der Valk, P., Kipp, M. (2012). Myelin debris regulates inflammatory responses in an experimental demyelination animal model and multiple sclerosis lesions. Glia, 60(10), 1468-1480.
11. Girardet, C., Bonnet, M. S., Jdir, R., Sadoud, M., Thirion, S., Tardivel, C., Troadec, J. D. (2011). Central inflammation and sickness-like behavior induced by the food contaminant deoxynivalenol: A PGE2-independent mechanism.Toxicological Sciences, 124(1), 179-191.
12. Hruška-Plocháň, M., Juhas, S., Juhasova, J., Galik, J., Miyanohara, A., Marsala, M., Motlik, J. (2010). A27 Expression of the human mutant huntingtin in minipig striatum induced formation of EM48+ inclusions in the neuronal nuclei, cytoplasm and processes. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 81(Suppl 1), A9-A9.
13. Brooks, S., Jones, L., & Dunnett, S. B. (2010). A29 Frontostriatal pathology in the (C57BL/6J) YAC128 mouse uncovered by the operant delayed alternation task. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 81(Suppl 1), A9-A10.
14. Yu, L., Metzger, S., Clemens, L. E., Ehrismann, J., Ott, T., Gu, X., Nguyen, H. P. (2010). A28 Accumulation and aggregation of human mutant huntingtin and neuron atrophy in BAC-HD transgenic rat. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 81(Suppl 1), A9-A9.
15. Baxa, M., Juhas, S., Pavlok, A., Vodicka, P., Juhasova, J., Hruška-Plocháň, M., Motlik, J. (2010). A26 Transgenic miniature pig as an animal model for Huntington’s disease. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 81(Suppl 1), A8-A9.
敬请关注玉研仪器微信号:yuyanbio 
您想了解更多详细资料吗?
请与我们联系:
TEL : 021-35183767 , 18502129044
QQ : 3007536034
Mail: yuyan0317@126.com
敬请来电咨询!

上海玉研科学仪器有限公司
品牌商实名认证
钻石会员
入驻年限:12年